2024/04/19 printed from http://dermboard.org All Rights Reserved
What is the most common cause of hair loss?
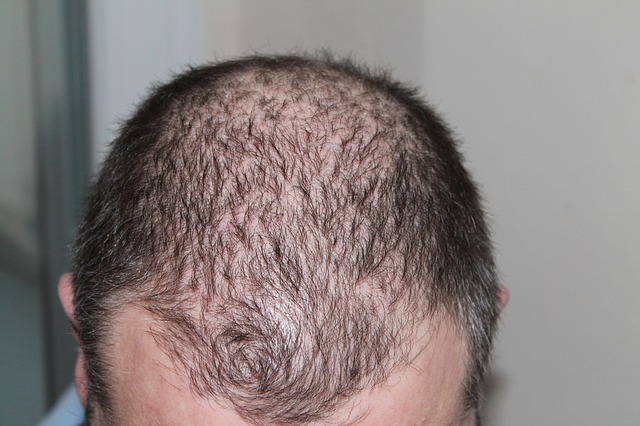
The most common cause of hair loss is so-called “androgenetic alopecia.†When it happens in males it is called “male-pattern hair loss†and when it happens in women it is called “female-pattern hair lossâ€. It is caused by still not completely understood interplay of genetics and influence of male hormones on hair follicles causing hair to become progressively shorter and thinner to the point of complete loss of hair (usually only in males).
-In men bald areas develop on the front and the top of the scalp.
-Women often have thinning of the hair (usually without complete hair loss) on the top of the scalp in so-called “Christmas tree-pattern†with preserved frontal hairline.
Another quite common cause of hair loss is called “alopecia areata†which is usually sudden loss of hair in oval to round patches. Please see a separate detailed description of this hair loss under “alopecia areata†tab. Hair loss can be caused by many other conditions such as poor nutrition, low iron, thyroid gland diseases, various infections, some medications etc.
What should I do if I notice hair thinning?
Since there could be numerous reasons for hair loss, you should see your health care provider for possible workup. The initial workup should include detailed story and timeline of your hair loss and detailed physical examination to possible additional workup if needed (e.g. blood work, skin biopsy using small punch instrument etc.).
What are the tests I should have?
In most cases other than a detailed story and the timeline of your hair loss with a detailed physical examination and list of medications at the time of hair loss, no tests are needed. However, if we cannot figure out the reasons for your hair loss, we usually check some of the following: complete blood cell count, thyroid function tests, ferritin levels, vitamin D levels, tests for syphilis, lupus test known as ANA etc.
What are the treatments for hair loss?
Treatments depend on the causes of your hair loss. Below are listed some options for the most common type of hair loss, i.e. androgenetic alopecia. Only two medications are FDA approved for hair loss and only for androgenetic alopecia.These are finasteride pill (brand name Propecia, available only with prescription) for male pattern hair loss (not approved for females), and minoxidil (brand name Rogaine, available without prescription) 5% liquid or foam for both males (gently massaged into the scalp twice daily) and females (gently massaged into the scalp once daily – but we recommend to our patients twice daily).
There are no other FDA approved medications for hair loss, but at the same we use many medications approved by FDA for other purposes (indications) to treat hair loss, again depending on reasons for hair loss.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) must be gently massaged into the scalp twice daily for at least two months to see its first effects. It will not be effective for everyone, but if effective you will first notice that your hair sheds less, and then in four to eight months you will notice increased hair growth. The effects of minoxidil reach plateau (i.e. point of no further improvement) after one to one and a half years of use, but must be continued forever, otherwise all improvement in hair density will disappear within 1-2 months. The average cost is about $10 per month.
As I have mentioned above, minoxidil may not work for everyone. Generally, the best results are seen when used within the first 5 years after you have noticed thinning of the hair, when it involves the crown (top) of the head, and when the surface area of hair loss is less than about 4 inches (10 centimeters) in diameter. Up to 4 in10 people (females and males) will have cosmetically good results with continuous use of minoxidil. Side effects and adverse reactions to minoxidil happen rarely, and thus far, none of my patients have experienced any (and I have exclusively been practicing dermatology since 2003). Per some studies, minoxidil may cause skin irritation, hand and feet swelling, faster heart beating, and weight gain. - Finasteride (Propecia) is a prescription pill that decreases the production of one of the male hormones that has been shown to be involved in promoting androgenetic alopecia (male- and female-pattern hair loss). Therefore this medicine increases hair density. This medicine is also used to decrease the size of prostate, but in 5 times higher doses. For hair loss you take it by mouth 1mg daily for at least 3 months. Even this low dose used for hair loss can rarely cause side effects, such as problems with erection and ejaculation, as well as decreased sex drive. This is one of the most quoted reasons by my patients to refuse the treatment with finasteride. This medication also needs to be used forever, otherwise all benefits of its use will disappear within one year after stopping it. Females should not use finasteride, since it can cause abnormal genitalia in the male babies; it has been connected with a chance of breast cancer; plus it has not been proven to help regrow hair in most women. Despite this, some of my colleagues use it in females who cannot get pregnant and who are desperate about their hair loss.
- Spironolactone (brand name Aldactone) is a prescription diuretic (“water pillâ€) that also decreases the production of one of the male hormones that has been shown to cause androgenetic alopecia (male- and female-pattern hair loss). Therefore this medicine may increase hair density. But it is not FDA approved for the treatment of hair loss, and it has so-called Black Box Warning stating that it can cause tumors in rats and to “only use for approved indications and avoid unnecessary use.â€Â Spironolactone should be avoided in females who can become pregnant, since it can cause birth defects. But it can be used in females who can become pregnant, if they use two contraceptive methods while taking this drug.
- Hair transplant. A great option for this type of hair loss is hair transplant which could be done traditionally using strip techniques (i.e. Follicular Unit Transplantation – FUT), where a strip of healthy hairs is removed from the back of scalp, then carefully cut in very small pieces under microscopes, and inserted into the balding scalp. A newer technique, which is getting more popular, is called Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), where each small follicular unit is removed from the back of scalp and inserted into the balding scalp. This technique does not require stitching and may be done robotically (ARTAS system).
- Psychological support. Many patients take hair loss very hard which is very understandable. Patients have to deal low self-esteem or feeling unattractive. But you are not alone and there are some good treatments including ever-improving hair transplant techniques. You should also speak to your health care provider and your friends about your feelings. Sometimes you will need a referral to a psychologist and almost always to some local support group, which can provide you with tips on cosmetic coverings if needed.
